In order to fully utilise the UniFi APs full feature set, you’ll need to have a UniFi controller of some sort. This can be a UniFi Cloud Key, a UniFi Cloud Gateway, or… you can host one yourself. So obviously, I chose the third option.
There are two methods for installing the controller. One is on Docker, or you can use a Bare-Metal install. I’ll go through both, but I personally use the Docker setup.
Docker
Well, in order to do this, you obviously need to have Docker installed - if not, see here for how to do that.
Compose file
version: "3.9"
name: unifi
services:
unifi-db:
container_name: unifi-db
image: mongo:3.6
environment:
- TZ=Etc/UTC
volumes:
- /srv/unifi/db:/data/db
- /srv/unifi/init/init-mongo.js:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/init-mongo.js:ro
networks:
- unifi
restart: unless-stopped
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "mongo", "--eval", "db.adminCommand('ping')"]
interval: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 5
unifi-network-application:
container_name: unifi-network-application
image: lscr.io/linuxserver/unifi-network-application:latest
depends_on:
unifi-db:
condition: service_healthy
environment:
- MONGO_DBNAME=unifi-db
- MONGO_HOST=unifi-db
- MONGO_PORT=27017
- MONGO_USER=unifi
- MONGO_PASS=pass
- PGID=1000
- PUID=1000
- TZ=Etc/UTC
ports:
- 3478:3478/udp
- 10001:10001/udp
- 8080:8080
- 8443:8443
- 8843:8843
- 6789:6789
volumes:
- /srv/unifi/network-application:/config
networks:
- unifi
- proxy
restart: unless-stopped
networks:
unifi:
driver: bridge
ipam:
config:
- subnet: 172.28.0.0/16
proxy:
external: true
/srv/unifi/init/init-mongo.js
db.getSiblingDB("unifi-db").createUser({
user: "unifi",
pwd: "pass",
roles: [{ role: "dbOwner", db: "unifi-db" }]
});
db.getSiblingDB("unifi-db_stat").createUser({
user: "unifi",
pwd: "pass",
roles: [{ role: "dbOwner", db: "unifi-db_stat" }]
});
You can change the password by changing pass to a value of your preference.
After this, run docker compose up -d in the directory you have placed the compose file in, and it should start running.
Now head to setup:
Bare-metal
This only works on Debian or Ubuntu machines, credit to https://community.ui.com/user/AmazedMender16/ed097858-e875-46ba-b9ea-7c65e2747440, for his script to do so.
Install pre-requisites
Ensure the ca-certificates package is installed.
sudo apt-get update; sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl -y
Download and execute script
curl -sO https://get.glennr.nl/unifi/install/install_latest/unifi-latest.sh && sudo bash unifi-latest.sh
Examples (if exposing directly)
curl -sO https://get.glennr.nl/unifi/install/install_latest/unifi-latest.sh && sudo bash unifi-latest.sh --email hello@848226.xyz --skip --fqdn unifi.848226.xyz
Exposing
With NGINX Proxy Manager
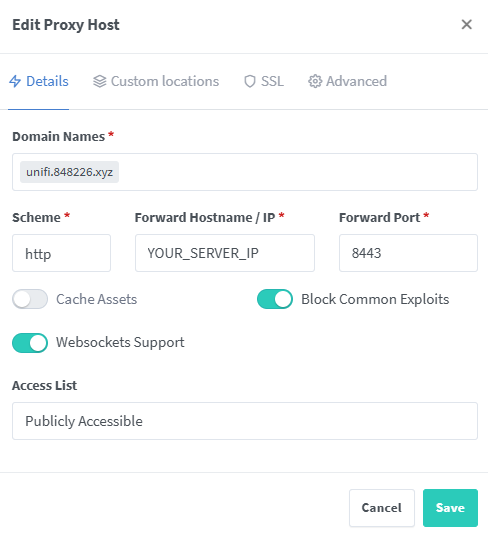
You will need to create a new Proxy Host.
Details
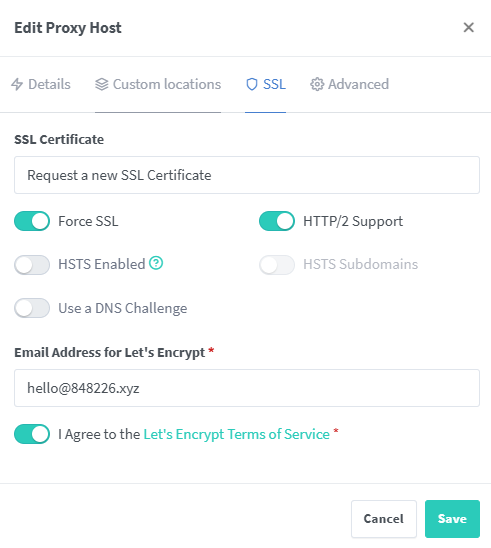
SSL
Advanced
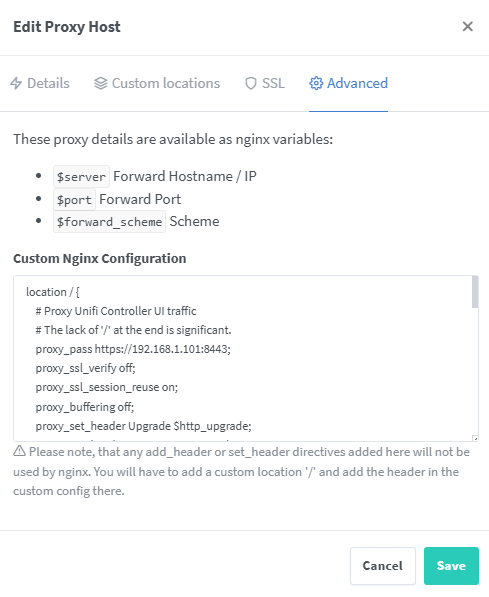
location / {
# Proxy Unifi Controller UI traffic
# The lack of '/' at the end is significant.
proxy_pass https://YOUR_SERVER_IP:8443;
proxy_ssl_verify off;
proxy_ssl_session_reuse on;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
## Specific to Unifi Controller
proxy_hide_header Authorization;
proxy_set_header Referer '';
proxy_set_header Origin '';
}
location /inform {
# Proxy Unifi Controller inform endpoint traffic
# The lack of '/' at the end is significant.
proxy_pass https://YOUR_SERVER_IP:8080;
proxy_ssl_verify off;
proxy_ssl_session_reuse on;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
## Specific to Unifi Controller
proxy_hide_header Authorization;
proxy_set_header Referer '';
proxy_set_header Origin '';
}
location /wss {
# Proxy Unifi Controller UI websocket traffic
# The lack of '/' at the end is significant.
proxy_pass https://YOUR_SERVER_IP:8443;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
## Specific to Unifi Controller
proxy_set_header Origin '';
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_hide_header Authorization;
proxy_set_header Referer '';
}
Directly exposing
Expose the following ports in your firewall (only port forward if you are running your UniFi controller off-site from your UniFi devices):
- 3478
- 10001
- 8080
- 8443
- 8843
- 6789
Setup
Now you must go through the setup process for the UniFi controller. In order to adopt new UniFi devices to your self-hosted controller, follow the following steps:
Connect
SSH to your UniFi Device, using it’s IP Address, which can be found in your router’s dashboard:
ssh ubnt@YOUR_DEV_IP
with a default password of ubnt
Set the inform URL
Get your controller IP Address, or the hostname which you are exposing it on, and run the following command:
set-inform http://YOUR_UNIFI_CONTROLLER/inform
Complete adoption
Head to your controller, login, click UniFi Devices in the sidebar, and you should see your device waiting for adoption.
Final Thoughts
I think self-hosting the UniFi controller is a great way to be able to use UniFi devices without having to purchase a dedicated controller, especially if you already have the infrastructure and knowledge in order to do so.